EasyPost
shipping label creation flow design + usability testing
Reimagined a cumbersome and lengthy form experience into a positive moment of accessible delight, efficiency and flexibility.
View prototypeRole: Research, Design, Prototypes
Team: 1 Designer, 2 Engineers, 20+ participants
Timeline: 2 Months
Slide left/right for before | after
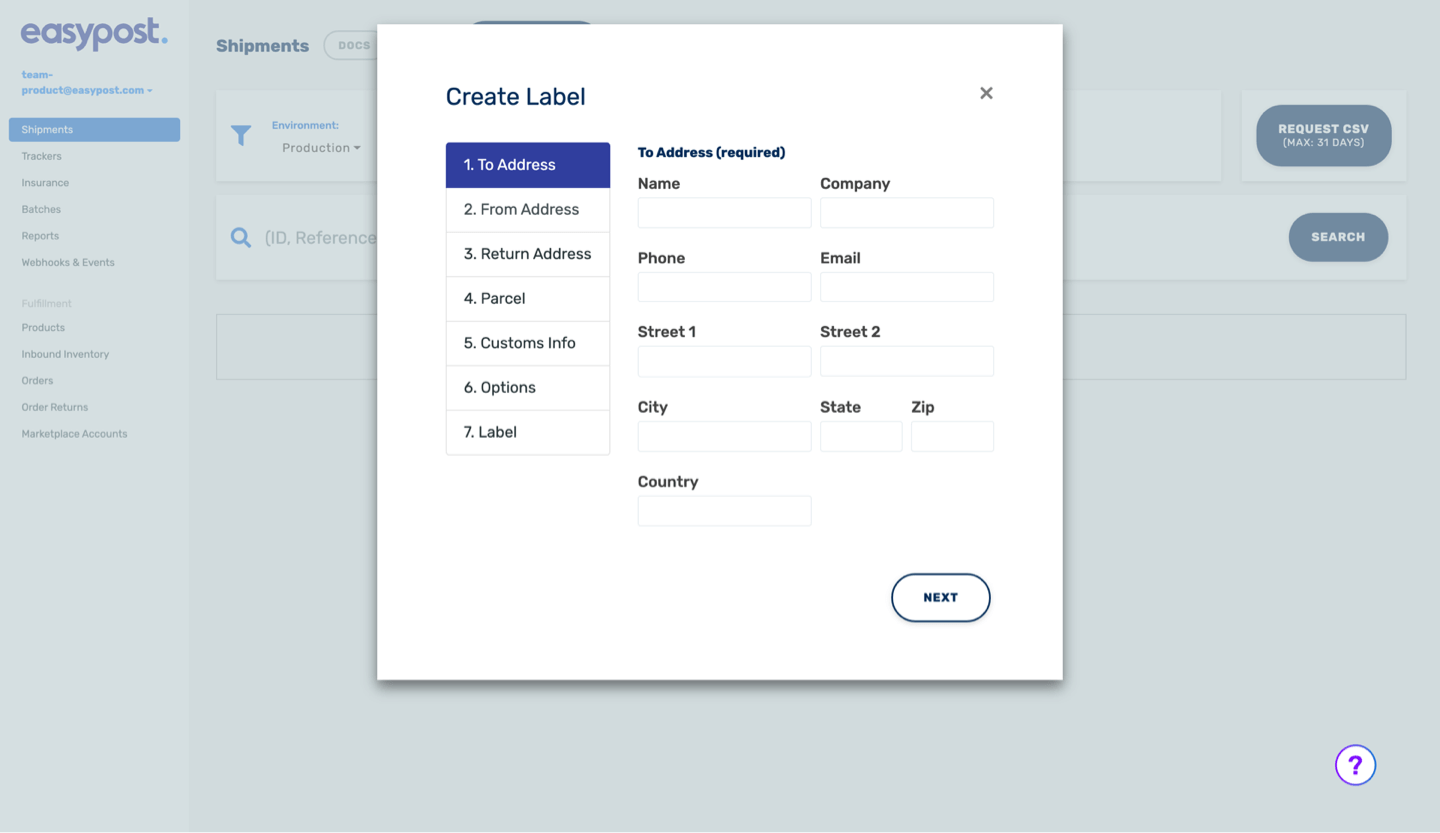
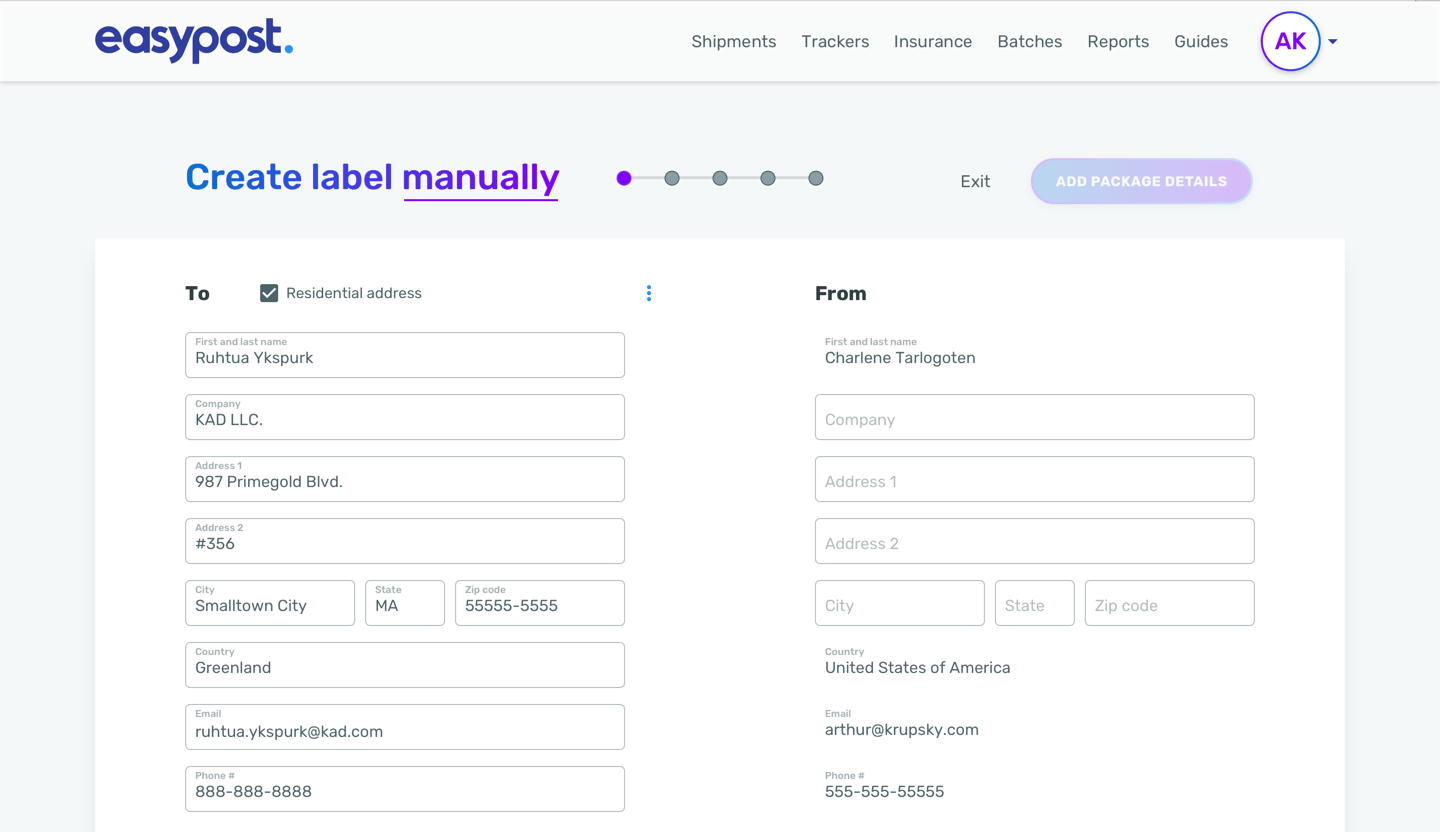
Modal (Original) v. Page (New)
Vision
Consistency and continuity in the user experience by keeping content within the same context. Users can navigate between pages seamlessly without interruptions or distractions caused by modals.
Users should have a clearer sense of context because they can see the content surrounding the current page. This helps users maintain focus and understand the relationship between different pieces of information.
Improved accessibility to provide a clear structure and navigation flow. Users who rely on screen readers or keyboard navigation can more easily navigate between pages and understand the content hierarchy.
Enhanced mobile responsiveness: Page-based UIs can be more easily optimized for mobile devices, as designers can create responsive layouts that adapt to different screen sizes. This ensures that content remains readable and usable across various devices without sacrificing user experience.
Better support for browser features such as history, bookmarking, and back/forward navigation. This allows users to easily revisit previously viewed pages and bookmark important content for future reference.
Reduced cognitive load: Page-based UIs can help reduce cognitive load by presenting content in a structured manner. Users can focus on one task or piece of information at a time without being overwhelmed by additional layers of interaction introduced by modals.
In many cases, loading a new page is faster than loading a modal, especially if the modal contains complex content or functionality. This can contribute to a smoother and more responsive user experience.
Values
By prioritizing these values during the design process, I convereted and created a UI with many steps and fields to just a few pages that effectively guided users through the process while providing a positive and intuitive experience.
Clarity: The UI should be clear and easy to understand, guiding users through each step with clear instructions and visual cues. Use descriptive labels, intuitive icons, and consistent navigation patterns to help users understand where they are in the process and what actions they need to take next.
Consistency: Maintain consistency in design elements, layout, and navigation throughout the UI to reduce cognitive load and enhance usability. Consistent use of colors, typography, button styles, and other UI components helps users feel familiar and comfortable as they progress through the steps.
Simplicity: Keep the UI simple and streamlined, avoiding unnecessary complexity or clutter that can overwhelm users. Prioritize essential information and actions, and eliminate any unnecessary steps or distractions to make the process as straightforward as possible.
Progress indication: Provide clear feedback on the user’s progress through the steps, such as progress bars, step indicators, or breadcrumbs. This helps users understand how far they’ve come and how much is left, reducing uncertainty and frustration.
Flexibility: Design the UI to accommodate different user preferences, devices, and screen sizes. Ensure that the UI is responsive and adaptable, providing a consistent experience across various devices and allowing users to complete the process at their own pace.
Feedback and validation: Provide immediate feedback when users interact with the UI, such as validating form inputs in real-time or displaying confirmation messages after completing a step. This helps users feel confident that their actions are being processed correctly and encourages them to continue.
Accessibility: Ensure that the UI is accessible to users with disabilities by following best practices for accessibility, such as providing alternative text for images, using semantic HTML markup, and ensuring keyboard navigation support.
User testing and iteration: Conduct user testing throughout the design process to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement. Iterate on the design based on user feedback, making adjustments to optimize usability, clarity, and efficiency.
Methods
We used several methods to identify whether the modal or page design is performing well:
Usability Testing: Conducted usability testing with real users to observe their interactions with the designs.
Heatmaps and Click Tracking: Visualized user interactions with the design.
A/B Testing: Performed A/B testing by presenting different versions of the design to users and comparing their performance or behavior.
Analytics Data: Analyzed quantitative data from web analytics tools to track user behavior, engagement metrics, and conversion rates. Found trends and patterns in user interactions.
Customer Feedback and Support Tickets: Monitored customer feedback channels to gather insights into user satisfaction and identify recurring issues or pain points with the new design implementation.
Obstacles
Disruption of workflow: Modal interrupt the user’s workflow by overlaying content on the current page.
Loss of context: When a modal pops up, it often obscures the underlying content, leading to a loss of context. Users may forget what they were doing on the main page or feel disoriented when the modal is dismissed.
Limited space: Modals have limited space, which can constrain the amount of information that can be displayed or the complexity of interactions that can occur within them.
Accessibility concerns: Modal can pose accessibility challenges, particularly for users who rely on screen readers or keyboard navigation. Navigating between the modal and the underlying content may be difficult for these users, leading to frustration and potential usability issues.
Mobile responsiveness: Modal is not optimized for mobile devices, where screen real estate is limited. This can result in poor user experiences on smaller screens, such as difficulty reading content or interacting with form fields, which there are a lot of.
Measures
We evaluated various aspects of the user experience and its impact on business goals:
Raise Task Success Rate and Speed up to 60%: Measured the percentage of users who successfully complete tasks and form.
User Engagement Metrics: Tracked user engagement metrics such as time spent on the page in the app, number of visits, page views, and interaction patterns.
Triple Retention and Lower Churn Rates by 40%: Measured user retention and churn rates to assess the long-term impact of the design on user loyalty and satisfaction. We reviewed metrics such as user churn rate, retention rate, and customer lifetime value (CLV) to understand user behavior over time.
Adherence to relevant standards of accessibility such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
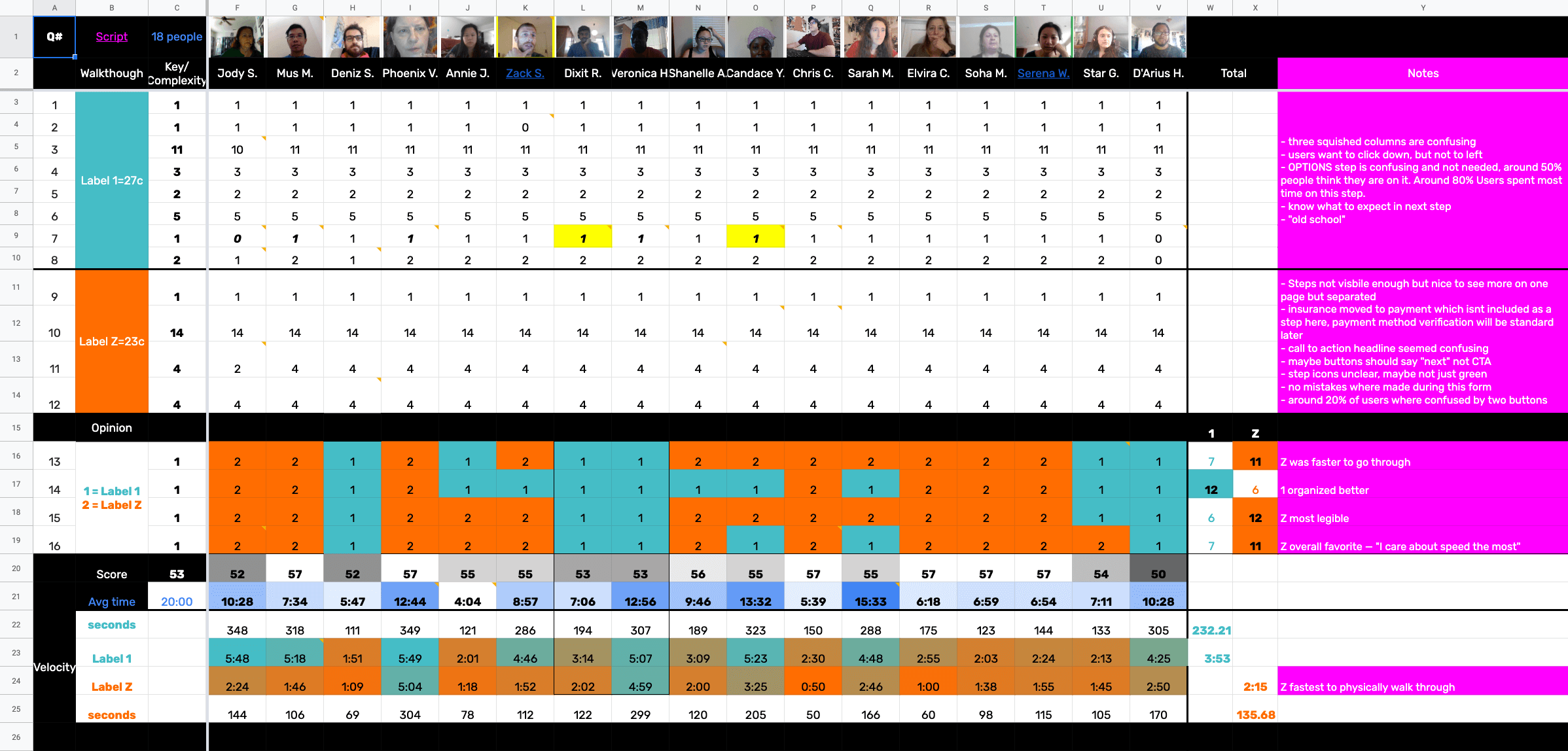
The usability test results in Pink
Modal is Teal and Page is Orange